The Biggest Challenge facing Oracle DBAs
It’s perhaps every Oracle DBAs biggest nightmare. The call at 3AM informing them that lagging performance in production databases is impacting the business. This challenge is amplified as companies are processing more and more data, supporting larger data sets, and putting tremendous demands on the databases tasked with managing it all.
DBAs leveraging Oracle databases are under intense pressure to deliver rapid response times to end users of applications while ensuring high levels of availability. In fact, a research study by Gleanster reported that 88% of IT professionals cited that the database was the most common challenge or issue with application performance.
More Performance with the New FlashArray//X
The new Pure Storage FlashArray//X Family delivers high performance coupled with fast response times and high availability, and can help make those late night phone calls a thing of the past. The Pure Data-Centric Architecture for Oracle solutions help customers achieve their plans for digital transformation, removing storage barriers of the past and opening up opportunities to enhance OLTP performance, modernize Oracle data warehouses, and begin taking on new projects around modern analytics.

Pure Storage FlashArray//X is the world’s first enterprise-class, all-NVMe flash storage array. It represents a new class of storage – shared accelerated storage (a term coined by Gartner) – that delivers major breakthroughs in performance, simplicity, and consolidation of mixed workloads. With latency as low as 250 μs, FlashArray//X’s all-NVME architecture brings new levels of performance to mission-critical business applications. With built-in Purity ActiveCluster, more applications can now benefit from the simple to deploy, always-on business continuity provided by via active/active metro stretch clustering. Pure DirectFlash™ with 100% NVMe also enables unprecedented performance density – the kind of density required for mixed-workload consolidation in your cloud. //X currently supports ultra-dense 18.3TB DirectFlash™ modules, for maximum density and full performance. In addition, Purity’s always-on and limits QoS features means you can consolidate radically diverse applications without fear of I/O contention.
The new FlashArray//X Family builds on the effortless and efficient performance and value introduced in 2015 with the FlashArray//M. In order to demonstrate the gains in transaction processing and reduction in latency, we ran tests comparing the latest FlashArray//X90R2 to a FlashArray//M70. Details and results of the testing follow.
//M vs //X: Oracle Performance test with SLOB
For this test, we compared a FlashArray//X90 to a FlashArray//M70 to compare relative performance and latency improvements with the newer array for data-intensive Oracle workloads. Both systems were running their respective Purity software releases at GA.
To generate and process more load, we used 8-node Oracle RAC environment hosting two databases, OLTP for online transaction processing workloads and DSS for processing data warehouse workload respectively.
Each database node is a commodity x86 server with 2 x Intel Xeon CPU E5-2697 v2 @ 2.70GHz with 12 cores each (totaling 24 cores), 512GB of RAM and 2 x 16Gb FC ports. The servers were installed with Oracle Linux 7.4 operating system, Oracle 12c Release 2 Grid Infrastructure and Oracle 12c Release 2 Database Enterprise Edition. Both FlashArrays //M70 and //X90 are connected and zoned into the database nodes and we created two sets of databases for each workload that were hosted on these FlashArrays.
OLTP workload profiles numerous random single-block reads and writes that requires lower latency, higher IOps (Input Output operations per second) whereas DW workload profiles numerous multi-block reads and writes that requires higher bandwidth from the underlying storage.
Data warehouse workload performance tests
To demonstrate high bandwidth, high throughput of data loads that are essential part of the data warehouse systems, we used a TPC-H like benchmark kit which provides tool to generate multi-terabyte, high cardinality data as well as set of business oriented ad-hoc queries that examine large volumes of data with a high degree of complexity, and give answers to critical business questions.
We generated the source data at a scale factor of 10,000 amounting to 10.85 TB of high cardinality data placed across multiple files.
Data Load performance tests
As part of the data load or data ingest test, the same 10.85 TB source data was first loaded onto the 8-node Oracle RAC database (DSSM70) hosted on FlashArray //M70 and later on DSSX90 database, hosted on FlashArray //X90. The following table illustrates the elapsed time and ingest rates observed across these two systems.
| Data Load Tests | Elapsed Time | Write Bandwidth | Ingest Rate |
| //M70 | 5579 seconds | 1.99 GBps | 7 TB/hour |
| //X90 | 1906 seconds | 5.83 GBps | 20.49 TB/hour |
| //X vs //M performance improvement | 65% faster | ||
Data Warehouse Query performance tests
As part of the data warehouse query performance test, we chose two queries from the available 22 queries and ran them across both the databases, DSSM70 and DSSX90. The first query went after the biggest table LINEITEM that was 7.3TB in size and the second query went after the second biggest table ORDERS that was 1.7TB in size. The following table illustrates the response time of the queries observed across two databases.
| DW Query Performance Tests | Elapsed Time | % Improvement | |
| //M70 | //X90 | ||
| Query 1 (Datasize – 7.3TB) | 809.48 sec | 604.39 sec | 25% faster |
| Query 2 (Datasize – 1.7TB) | 191.7 sec | 148.11 sec | 23% faster |
Bandwidth comparison of Data warehouse workloads
| Bandwidth Comparison | //M70 | //X90 | % Improvement |
| Read Bandwidth | 9.24 GBps | 12.38 GBps | 33% faster |
| Write Bandwidth | 1.99 GBps | 5.83 GBps | 193% faster |
Overall, for data warehouse type workloads that profiles high bandwidth of reads and writes, FlashArray //X90 offers the highest write rate of 5.83 GBps which is 193% faster than FlashArray //M70, while the read bandwidth around 13GBps, that is 33% faster than the prior model.
OLTP workload performance tests
OLTP workload profiles numerous random single-block reads and single-block writes along with REDO logging I/O. We used SLOB (Silly Little Oracle Benchmark), an Oracle I/O workload generation toolkit to generate varying I/O workloads to test the performance and scalability of the Pure FlashArray //X90 against //M70.
Two databases for OLTP workload, SLOBX90 and SLOBM70 were configured on //X90 and //M70 FlashArray systems. SLOB was configured to run against all the 8 RAC nodes and the concurrent users were equally spread across all the nodes. The following tests were performed:
- Users scalability test with 128 and 256 users across 8 Oracle RAC nodes
- Varying workloads
- 100% reads
- 90% reads, 10% writes
- 70% reads, 30% writes
The following graph shows the users scalability in terms of IOPS while running the SLOB workload for 128 and 256 users. Consistently we see the IOPS numbers higher on FlashArray //X90 than FlashArray //M70.
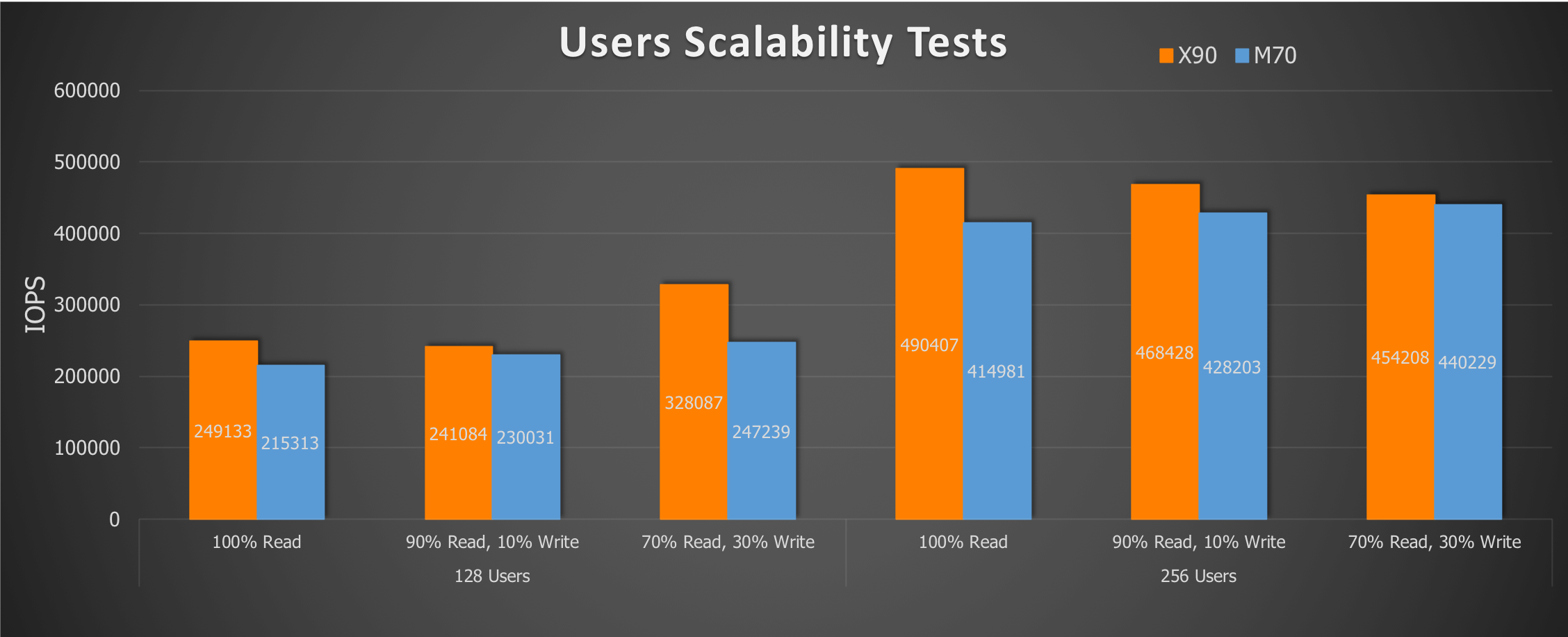
Lower IO latency can also improve the scalability and the following graph shows the latency of random single-block reads (db file sequential read) which is lower on FlashArray //X90 than //M70.

Overall, the OLTP performance tests shows lower latency in the range of 15% to 25% across varying workloads on //X90 than //M70 which is proportional to the improved IOPS numbers on //X90 than //M70. Any reduction in I/O latency gives valuable time back to the application resulting in meaningful gains to the business.
Conclusion
The test results demonstrate that the new FlashArray//X90 is setting a new bar for Oracle Database in density and performance for both OLTP and OLAP/DSS workloads, delivering faster response times at lower latency and higher bandwidth. Pure’s Evergreen™ subscription model means existing customers on //M arrays can upgrade non-disruptively to the //X, and avoid purchasing the same storage density twice. New customers have even more options for configuration and performance with the //X when sourcing storage from Pure, allowing them to take advantage of the next step in technology with NVMe and DirectFlash™.
The results are clear: If you are a DBA responsible for managing or deploying Oracle databases, the Pure Data-Centric Architecture will deliver the performance gains you need to meet the challenges of today’s business environments. All-flash solutions from Pure Storage are as important to the Oracle database as the Oracle database is to the business.
For more information on announcements this year at Pure//Accelerate, check out our overall launch blog, Data Centric Architecture Powers Digital Business.






