If you’re looking for the most simplified snapshot as a backup solution or a solution that limits the backup IOPS on primary storage to save network bandwidth, you’re in the right place. You can achieve all this and even more with Veeam Pure Storage snapshot integration.
Veeam Universal storage integration for Pure Storage has vadarious options such as backing up the primary application, performing volume snapshots of applications, and replicating the snapshot to another site. The application can be further protected from ransomware attacks with SafeMode™ enabled either on the primary storage array or on the replication target.
Snapshot-only jobs create a chain of storage snapshots on the primary storage array and optionally perform the replication to the secondary Pure storage array for longer retention and disaster recovery purposes. To successfully run the snapshot-only jobs and asynchronous replication of the snapshots to another Pure Storage FlashArray™, you need to first configure the asynchronous replication and protection group setup of the primary storage FlashArray.
What Is Asynchronous Replication?
Asynchronous replication leverages Purity snapshots. A snapshot is created on the source, and that snapshot is transferred to the replication site. The first transfer, known as the baseline, is a complete transfer of the entire contents of the volume. After the baseline copy is performed, the replication process performs incremental transfers by identifying the change data in the baseline and next snapshot.
What Do You Need to Run a Veeam Replication Job?
For Veeam to run the replication job, you would need to install Veeam 12 and install the Veeam Plugin V2 for Pure Storage. To successfully configure the replication, review the requirements for replication on Pure Storage. A protection group is configured on the primary array with the right volume enrolled for snapshot replication.
Check out the following video to learn how you can configure a Pure snapshot replication job on Veeam.
How to Set Up Asynchronous Replication
Asynchronous replication can be configured using the Purity web GUI, CLI, or by REST API. Configuring replication using the GUI is very straightforward. Configuring replication consists of the following high-level actions:
- Review the requirements for replication
- Connect the source and target array
- Create a protection group and add a secondary FlashArray
- Add volumes for the corresponding virtual machines to the protection group
Asynchronous replication requires the following configuration items before proceeding with replication:
- The source and target arrays must be connected to Ethernet switches. Direct connecting two storage arrays for replication is not supported.
- Each FlashArray must have four physical replication interfaces with two per controller or a replbond interface configured with the replication service assigned. The replication interfaces can be managed in the Settings > Network tab as shown below.
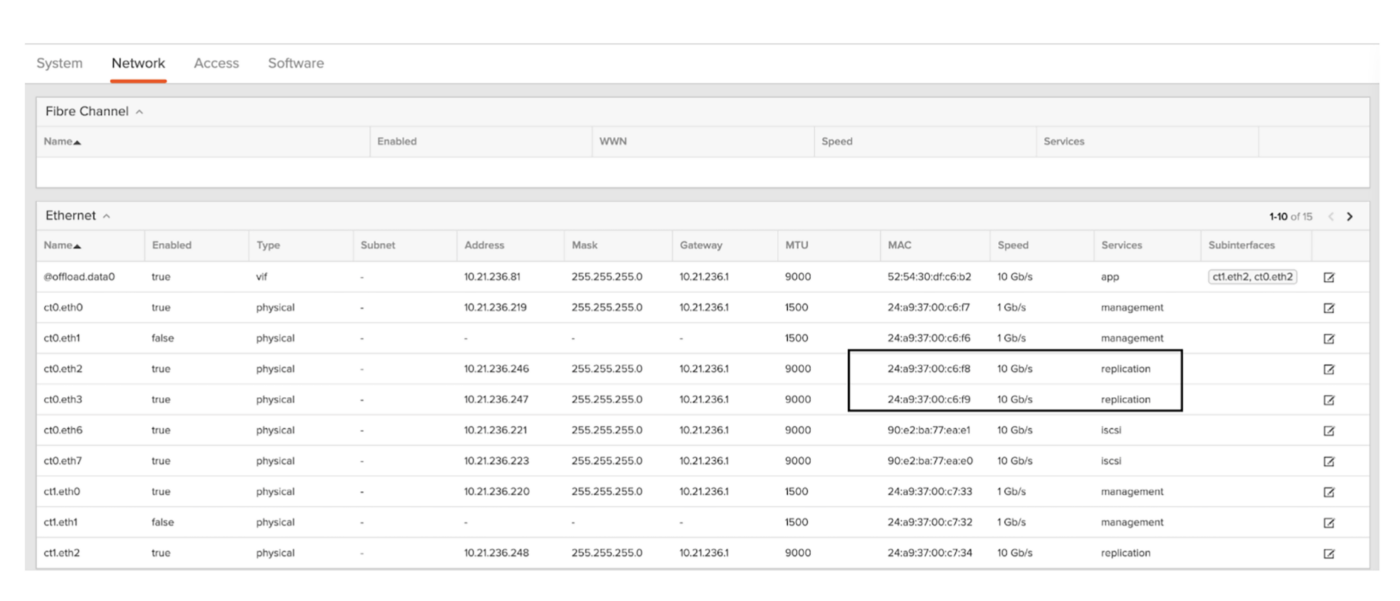
Figure 1: Managing the replication interfaces from the Network tab.
Note: If replbond is used, a mix of 1GbE, 10GbE, and 25GbE ports are not supported in the same replication replbond interface.
Connecting Arrays
To configure asynchronous replication, you’ll first need to connect the source and target arrays. Connecting arrays is a one-time process for each pair of peer arrays. For more information on multiple array connections, please refer to the Pure Storage asynchronous replication knowledge base article.
Arrays can be connected from either the source or the target. Regardless of which array you use to create the connection, you must make a note of the other array’s management IP or fully qualified domain name and get a connection key from the array you’re connecting to.
In this example, we’ll be performing the connection from a source FlashArray sn1-m70-d02-12 to a target FlashArray sn1-m70-d02-01. This means we’ll need to provide the management IP address and obtain a connection key from the target FlashArray sn1-m70-d02-01 array. On the target FlashArray, click Storage, then select the Array tab. Click the Configuration button in the lower right corner of the Connected Arrays window and select Get Connection Key as shown in the screenshots below.
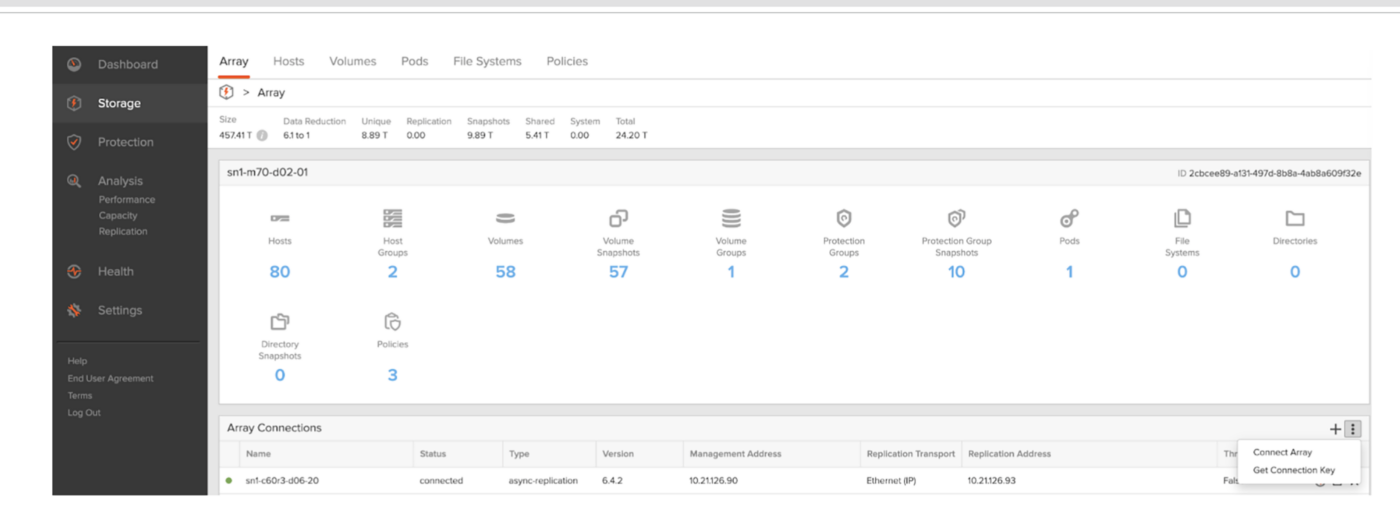
Figure 2: Getting the connection key from the target FlashArray to build the replication relationship.
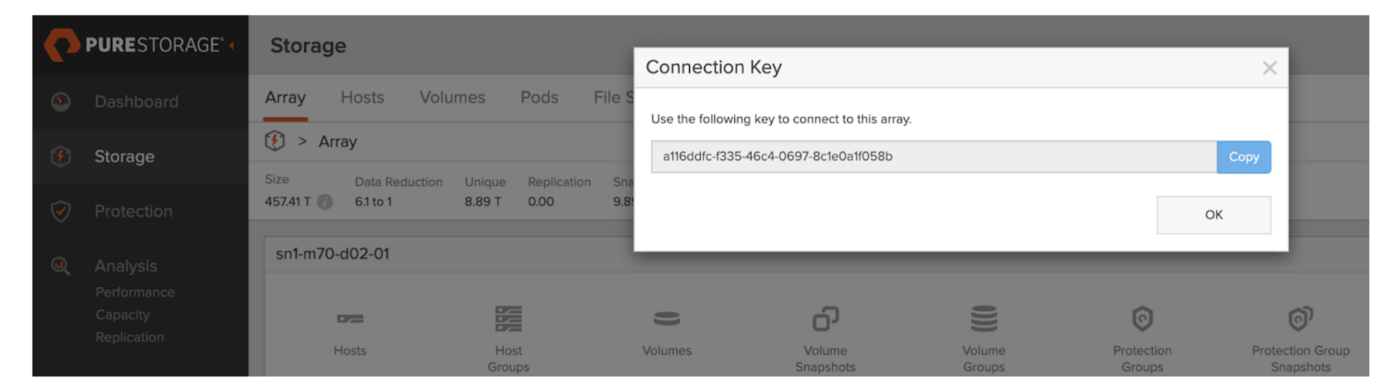
Figure 3: The connection key from the target FlashArray.
On the source FlashArray, click Storage, then select the Array tab. Click the + button in the lower right corner of the Connected Arrays panel. A Connect Array dialog window will open as shown in the screenshots below.
Figure 4: Array tab.
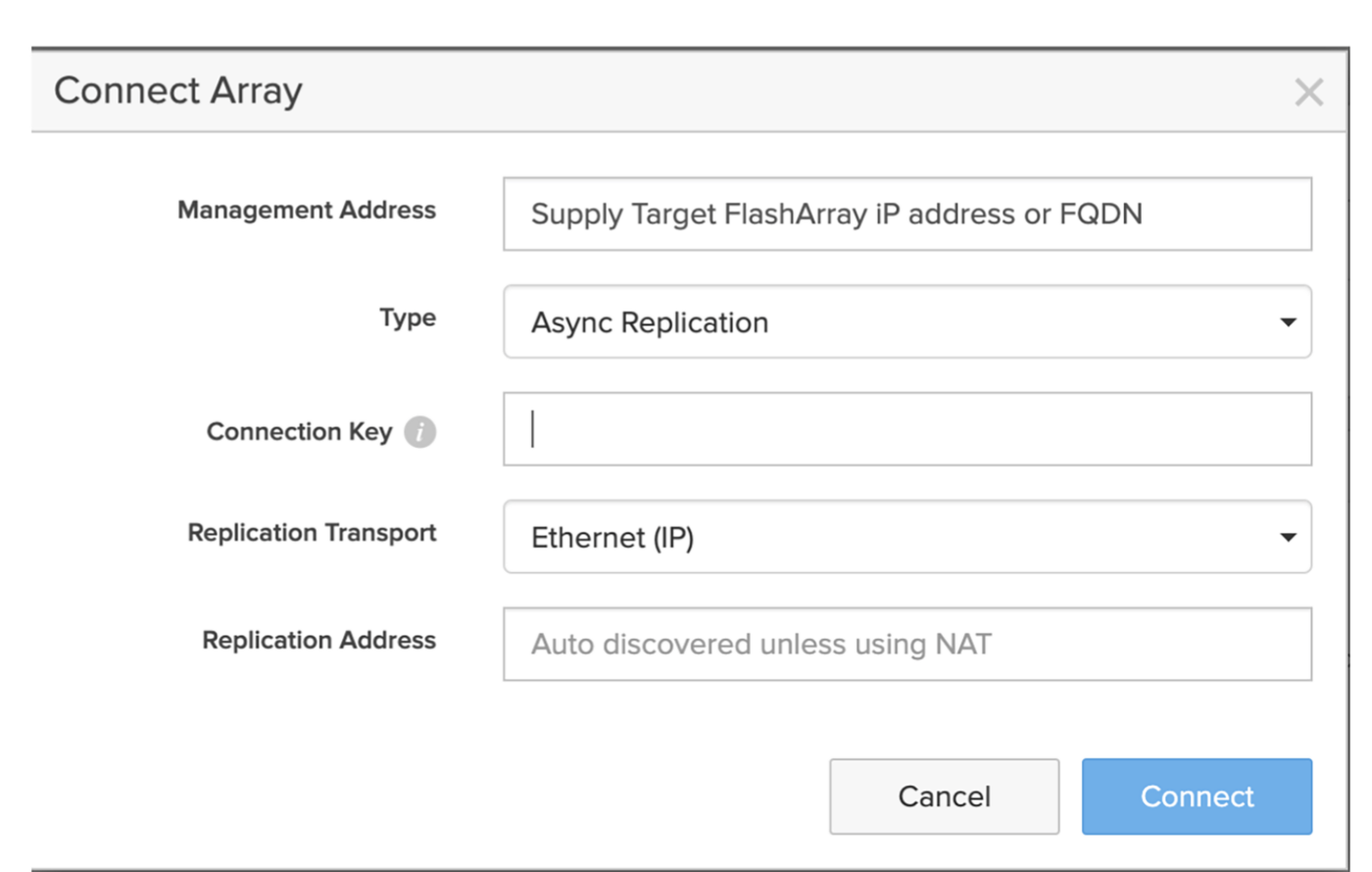
Figure 5: Connect Array dialog window.
Enter the management IP address or FQDN of the target FlashArray into the Management Address field and paste the connection key from the target FlashArray into the Connection Key field, and click Connect. This will set up the asynchronous replication relationship between the arrays.
Once the replication connection is set up successfully, for Veeam to perform the replication for the Veeam snapshot jobs, it’s mandatory to create a protection group. You would need to enroll the appropriate storage volumes (which are associated to the virtual machines in the Veeam job) into the protection group with the replication target configured.
How to Solve One of the Biggest Data Protection Challenges
Protection Group
A protection group, aka pgroup, defines a set of volumes, hosts, or host groups, which will be replicated together with point-in-time consistency across the member volumes. Replication in Purity is snapshot based, so each time Veeam job replication occurs, a snapshot is created. Each pgroup snapshot consists of one snapshot per volume for each of the volumes contained within that pgroup. For the Veeam integration, all the volumes in the pgroup will have a snapshot created that is point-in-time consistent with all of the member volumes in that pgroup and it will be controlled by Veeam for replicating to the target array. A protection group must be created on the source array as shown in the screenshot below.
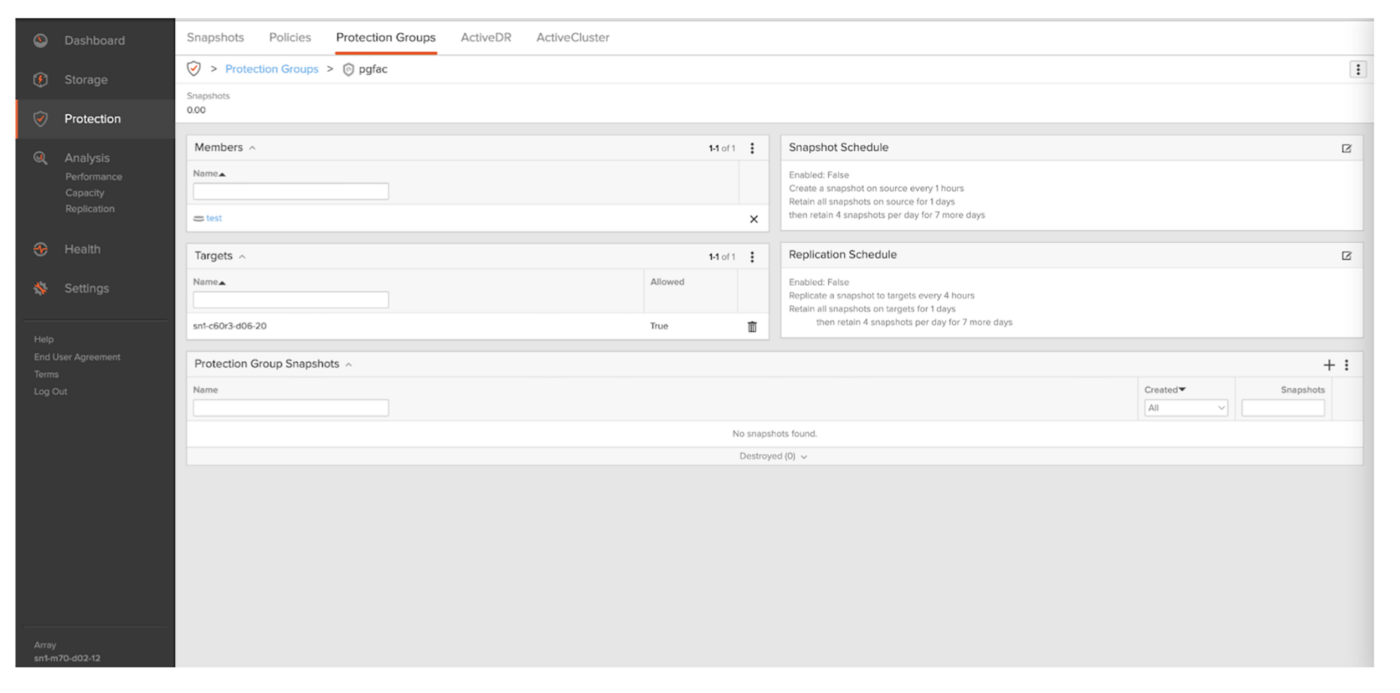
Figure 6: Creating a protection group on the source array.
Value Proposition
The following are business implications from Veeam replication to secondary storage:
- Limits the IO and network bandwidth on the primary storage, and snapshot backups can be performed from the replica target array
- Ability to restore to primary storage using reverse replication of snapshots to the original source
- Replication snapshot can be converted into a new volume and can be exposed as a new datastore to service dev/test purposes
- Instant recovery of the virtual machine from the replica target array






