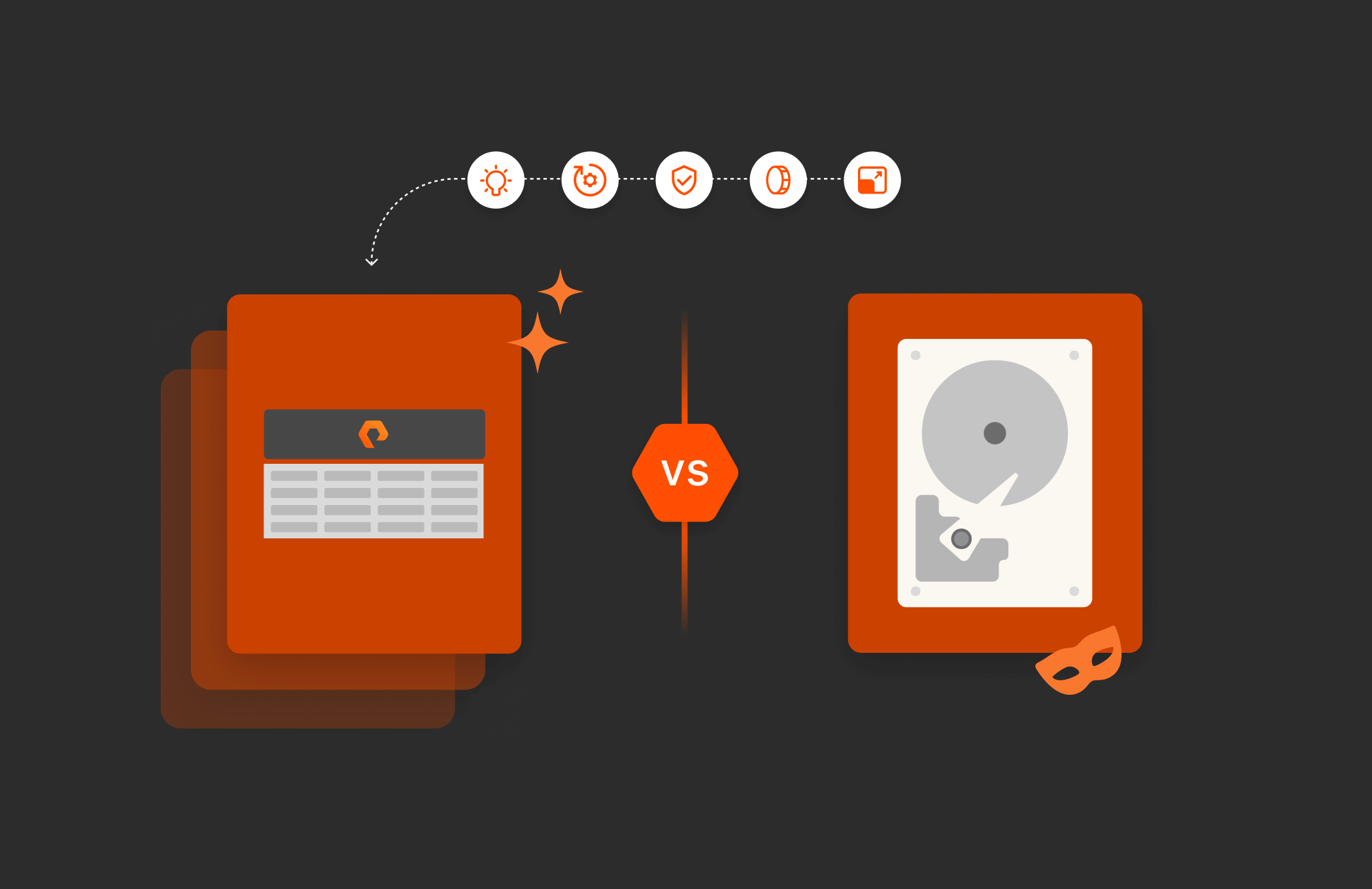
It’s no secret data growth is on the rise. Research from Enterprise Strategy Group indicates that data capacity will grow tenfold by 2030, which means there’s never been a better time to ditch spinning disk and make the switch to an all-flash data center. Disk vendors claim they can meet this challenge, but as the cost of energy, management, and upgrades associated with disk storage platforms continues to rise, how much is myth?
Myth 1: All-flash Is More Expensive than Disk
The myth that all-flash storage is more expensive than disk storage is increasingly being debunked as the total cost of ownership (TCO) for all-flash arrays becomes more competitive. While the initial purchase price of flash storage was once a significant barrier, advancements and economies of scale have brought prices down, making all-flash solutions a viable option for many organizations. When evaluating TCO, it’s essential to consider not just the upfront costs but also the operational expenses associated with power, cooling, and maintenance.
Contrary to common belief, when considering management, power, cooling, and replacement costs, all-flash storage emerges as a cost-effective solution with potential operational cost reductions of up to 60% and lower TCO by up to 40% over six years. All-flash storage arrays, such as those offered by Pure Storage, have been shown to significantly lower TCO compared to equivalent capacity hard disk drive (HDD) arrays. This reduction in TCO comes from various factors including the decreased need for physical space, as flash storage’s compact size allows data centers to condense equipment significantly.
Also, the perception that all-flash storage is prohibitively expensive fails to account for the operational efficiencies and cost savings it offers over time. Flash storage’s superior performance in terms of access times, lower latency, and higher throughput makes it ideal for performance-sensitive workloads, further justifying its cost against traditional HDDs.
Moreover, the power consumption advantage of all-flash arrays is a critical factor in reducing operational costs. All-flash solutions require up to 80% less power and space than HDDs, which translates into direct savings in electricity bills and cooling costs. These savings are compounded in hyperscale and enterprise data centers where reducing power consumption per rack is crucial from both a financial and environmental standpoint. The lack of moving parts in flash storage also means there’s less wear and tear over time, potentially reducing replacement costs and further decreasing TCO.
A comprehensive TCO comparison requires looking beyond simple cost-per-gigabyte metrics to include factors such as IOPS per watt and the performance and capacity per rack unit. Solid-state drives (SSDs), with their advantages over HDDs in these areas, often present a more cost-effective solution when all factors are considered. As the technology continues to evolve and prices decrease, all-flash arrays are becoming an increasingly sensible investment for organizations looking to optimize their data storage solutions.
Myth 2: HDDs Require Less Power than Flash
Sustainability initiatives highlight the inefficiencies of HDDs in terms of power usage, space requirements, and overall energy consumption.
The power consumption between HDDs and SSDs significantly differs, with SSDs being more energy efficient. HDDs use about 4-5 watts in write/read mode and 2-3 watts in idle mode. In contrast, SSDs consume less, with about 3.5 watts in write mode, 2 watts in read mode, and even lower in idle mode. This lower power consumption of SSDs not only saves energy but can also extend the battery life of laptops, making SSDs a more sustainable choice. All-flash storage, with technologies like Pure Storage® DirectFlash®, significantly reduces power and space needs by up to 80%.
Keep up with the latest innovations to the Pure Storage platform.
Myth 3: HDD Capacity Can Scale with Data Growth
In the evolution of storage solutions, HDDs have seen innovations like helium-sealed drives and shingled magnetic recording (SMR), enhancing capacity and reliability while reducing power consumption. Meanwhile, SSDs continue to evolve with new form factors and performance capabilities, making them suitable for a range of complex enterprise workloads and cloud infrastructure needs. The introduction of NVMe has further advanced SSD performance, offering low latency data paths and high throughput, beneficial for high-performance compute applications.
However, with data growth outpacing HDD capacity enhancements, organizations face challenges in scaling storage infrastructure efficiently. All-flash solutions provide seven times the density of HDDs, ensuring scalability that aligns with data growth rates.
As organizations strive to manage increasing data volumes and complex workloads, the choice between HDDs and SSDs is becoming more about finding the right solution for specific application and business needs, moving beyond mere comparisons of density and scalability.
Myth 4: HDDs Are Sufficiently Reliable
The reliability of HDDs decreases with age, leading to higher failure rates. All-flash storage guarantees superior uptime and reliability, making it a dependable choice for critical data storage needs.
It’s well-documented that SSDs tend to have lower failure rates compared to HDDs over time.
For instance, a study by Backblaze, a cloud storage provider known for publishing hard drive reliability statistics, has shown that SSDs generally exhibit lower annualized failure rates (AFR) than HDDs. While specific numbers vary, SSDs often have AFRs well below 1%, whereas HDDs can show failure rates significantly higher, depending on their make, model, and usage conditions. The reduced failure rate of SSDs is attributed to their lack of moving parts, which makes them less susceptible to mechanical failures that can affect HDDs, especially under conditions of high usage or physical shock.
Additionally, SSDs have been found to maintain their reliability over time better than HDDs, with failure rates not increasing as sharply as the drives age. This reliability is crucial for critical data storage needs where uptime and data integrity are paramount.
The consensus across multiple studies and real-world usage reports aligns with the view that SSDs offer superior reliability compared to HDDs, especially as they age. This makes SSDs a more dependable choice for critical data storage needs.
Myth 5: HDDs Are Easy to Upgrade
Upgrading HDD-based systems can be more cumbersome and disruptive than many anticipate. This is due in part to the mechanical nature of HDDs, which involves moving parts like spinning platters and read-write heads. These components make HDDs more vulnerable to physical damage and wear over time, complicating upgrades and replacements. Moreover, HDDs’ reliance on physical movement for data access and storage inherently limits their speed and durability compared to SSDs, which use flash memory to quickly access data without moving parts.
On the other hand, SSDs, particularly those equipped with technologies like on-drive Linux, offer a more seamless upgrade path. They’re designed for easier integration into existing systems, allowing for upgrades without significant downtime or disruption to operations. The incorporation of on-drive Linux enables SSDs to process data locally, reducing data transfer needs and improving overall system performance. This approach not only simplifies the upgrade process but also enhances the scalability and efficiency of storage solutions.
Furthermore, SSDs offer non-disruptive upgrades, meaning systems can be updated or expanded without taking them offline, a significant advantage over HDDs. This capability ensures continuous operation and productivity, a critical factor for businesses relying on constant data availability and system reliability.
While HDDs may present an initially less expensive option with higher base storage capacity, the long-term benefits of SSDs, including ease of upgrade, better performance, and increased reliability, make them a compelling choice for modern storage needs. The transition to SSDs from HDDs represents a shift toward more sustainable, efficient, and future-proof data storage solutions, aligning with the increasing demands for faster, more reliable, and easily upgradable storage infrastructure.
The Inevitable Growth of Data and the All-flash Solution
The era of relying on traditional hard disk drives is coming to an end. As data capacity is projected to grow tenfold by 2030, the shift toward all-flash data centers presents a sustainable and economically viable solution.
Unlike traditional HDDs, all-flash systems offer scalability and reliability without the soaring costs associated with energy management and upgrades. With the advantages of all-flash storage, from cost savings and sustainability to scalability and reliability, the shift toward all-flash data centers is not just a trend but a necessary evolution for future-proofing data storage.
The Pure//E Family: Making All-flash Accessible
The Pure//E™ family of products delivers scalable, sustainable, and environmentally friendly all-flash solutions at competitive costs. With the promise of lower power consumption, fewer drives, and continuous updates through Pure Storage Evergreen®, transitioning to an all-flash data center is now more accessible than ever.
Explore the benefits of the Pure//E family for your data storage needs and embrace the all-flash revolution for a sustainable, reliable, and cost-effective data center solution.

Written By:
Ditch Spinning Disks
Embrace the all-flash revolution for a sustainable, reliable, and cost-effective data center solution.