Summary
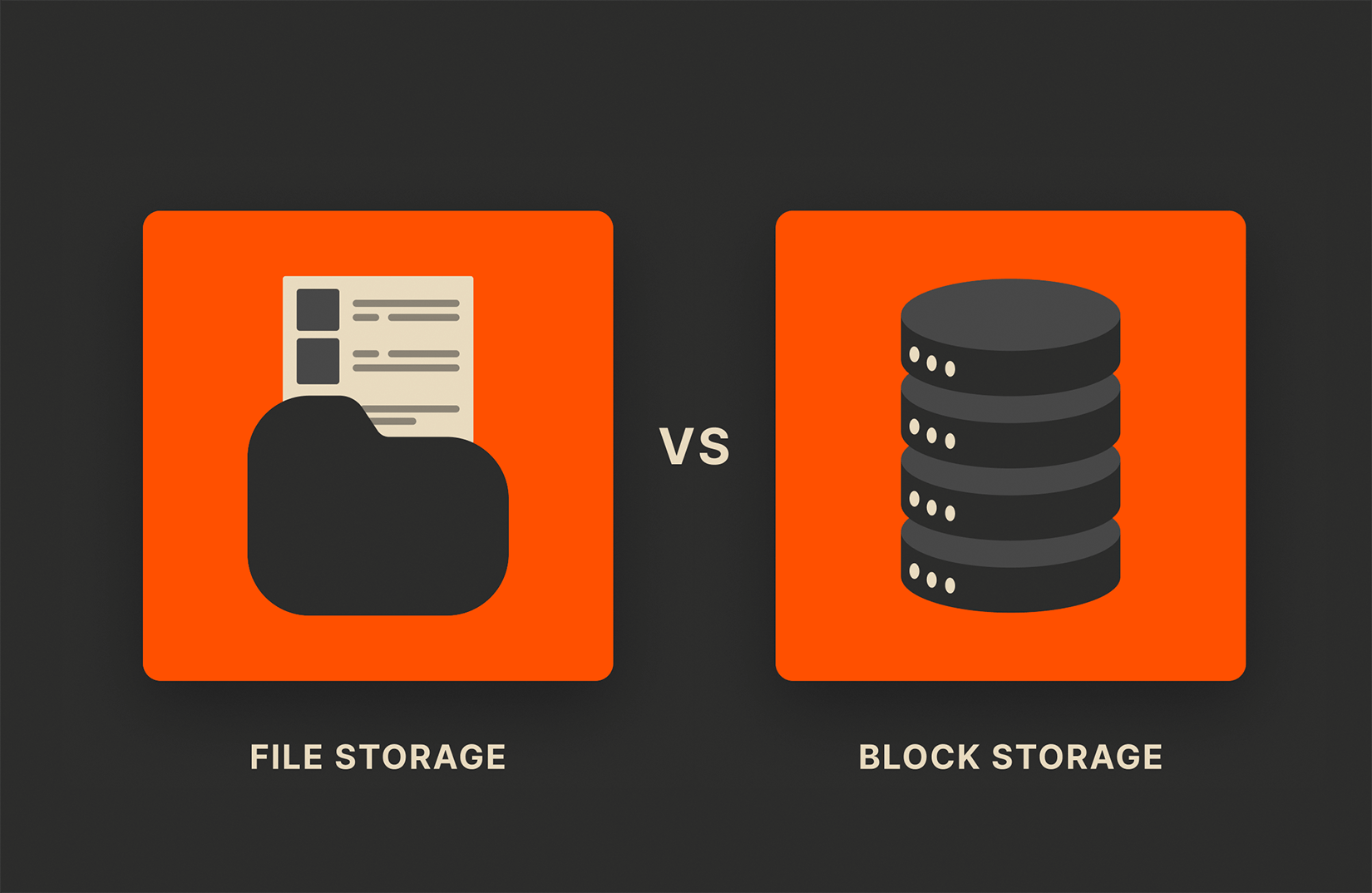
File storage organizes and stores data using a hierarchical structure, while block storage breaks data into fixed-size blocks.
Choosing the right storage solution is critical for efficiently managing and securing vast amounts of data. Two popular storage architectures—file storage and block storage—serve distinct purposes, each with its own advantages. Understanding these storage types and knowing how to choose between them is essential for optimizing your business’s data management strategy.
What Is File Storage?
File storage, also known as file-level storage, is a hierarchical storage system that organizes and stores data in a file and folder structure. Each piece of data is saved as a file, identified by a name and path, and managed through a system like Network File System (NFS) or Server Message Block (SMB). File storage is intuitive and user-friendly, making it the go-to choice for many everyday applications.
Key Characteristics of File Storage:
- Hierarchical: Data is stored in directories and subdirectories, mimicking traditional paper filing systems.
- Accessible: Files can be accessed, modified, and shared across networks by multiple users.
File storage is ideal for shared drives, document management, media libraries, and network attached storage (NAS) devices.
What Is Block Storage?
Block storage, also known as block-level storage, takes a different approach by breaking data into fixed-size blocks. Each block operates independently and can be stored across multiple locations. Block storage does not involve a file system directly; instead, it’s managed by the operating system. This method allows for more granular control over data and is often used in cloud environments and enterprise-level applications.
Key Characteristics of Block Storage:
- Granularity: Data is split into individual blocks, which can be accessed and managed separately.
- Flexibility: Blocks can be formatted to work with various file systems or databases.
Block storage is preferred for high-performance applications, databases, virtualization, and storage area network (SAN) environments.
Benefits of File Storage
File storage is widely used due to its simplicity and ability to support collaborative environments. Here are some of its key benefits:
- Ease of use: File storage’s familiar directory-based structure makes it easy for users to store, locate, and share files without specialized knowledge.
- Cost-effective: For organizations that need to store and share large volumes of unstructured data (e.g., documents, images, videos), file storage offers an affordable solution.
- Collaboration-friendly: Multiple users can access and modify files simultaneously, making it ideal for collaborative work environments.
- Compatibility: File storage systems are compatible with a wide range of devices and operating systems, offering broad accessibility.
Benefits of Block Storage
Block storage is known for its performance, flexibility, and scalability, making it a strong contender for businesses with more complex needs. But really the only key benefit of block storage over file storage is latency optimization. Block storage provides fast data access and low latency, making it ideal for applications requiring quick and consistent performance.
File Storage vs. Block Storage: How to Choose?
When deciding between file storage and block storage, your choice should be driven by your specific business needs, the nature of the data you’re working with, and the performance requirements of your applications.
Here’s a breakdown to help guide your decision:
Choose file storage if:
- You need simple data management: If your business relies on a file and folder structure for managing documents, images, and media, file storage is a straightforward and effective solution.
- Collaboration is key: If multiple users need to access and modify files regularly, file storage is ideal for facilitating easy sharing and collaboration.
- Cost is a concern: For businesses with large volumes of unstructured data that don’t require high performance, file storage is often the more economical option.
Choose block storage if:
- Your focus is on latency optimization: If your applications require fast and low-latency access to data, such as databases, virtualization, or high-performance computing, block storage is potentially a better choice.
Pure Storage for Unified File and Block Storage
File storage and block storage both offer valuable advantages depending on your specific business requirements. File storage is best suited for everyday applications where simplicity and cost-effectiveness are paramount, while block storage excels in high-performance environments where flexibility, speed, and scalability are critical. By carefully evaluating your data storage needs and future growth plans, you can select the storage solution that best aligns with your business goals.
To make file and block storage as easy and cost-effective as possible you can use Pure Storage® FlashArray™, which is optimized for performance, capacity, and scale, so you won’t have to choose between file or block storage and can take full advantage of both. ur specific business requirements. File storage is best suited for everyday applications where simplicity and cost-effectiveness are paramount, while block storage excels in high-performance environments where flexibility, speed, and scalability are critical. By carefully evaluating your data storage needs and future growth plans, you can select the storage solution that best aligns with your business goals.To make file and block storage as easy and cost-effective as possible you can use Pure Storage®FlashArray™, which is optimized for performance, capacity, and scale, so you won’t have to choose between file or block storage and can take full advantage of both.
The Innovation Race
Reducing Risk and Navigating the AI Frontier for Future Success
Dynamic Storage
Make file and block storage as easy and cost-effective as possible.
![]()