You might be wondering a few things about Veritas NetBackup Media Server Deduplication Pool (MSDP). For instance:
- How does NetBackup MSDP work with Pure FlashBlade®?
- How do you configure NetBackup MSDP on FlashBlade NFS?
- What are the benefits of having FlashBlade as a storage target?
This post will help answer many of these questions. Veritas and Pure recently worked closely to support MSDP over NFS on FlashBlade with direct availability from Veritas. In this post, I’ll walk you through the implementation process of the solutions for both existing and new NetBackup users.
NetBackup MSDP
Veritas NetBackup provides deduplication options that let you deduplicate data everywhere, as close to the source of data as you require. MSDP enables you to reduce:
- The amount of data that is stored
- Backup bandwidth
- Backup windows
- Infrastructure
With the MSDP option, you can choose at which point in the backup process you want to perform deduplication. NetBackup can manage your deduplication wherever you implement it in the backup stream. With media-server deduplication, the NetBackup client software creates the image of backed-up files as it would for a normal backup. The client sends the backup image to a media server, which hosts the plug-in that duplicates the backup data. The media server can be the storage server or a load-balancing server if one is configured. The deduplication plug-in breaks the backup image into segments and compares the segments to all the segments stored in that deduplication node. The plug-in then sends only the unique segments to the NetBackup Deduplication Engine on the storage server. The Deduplication Engine writes the data to an MDSP.
A storage server is an entity that writes to and reads from the storage. One host functions as the storage server, and only one storage server exists for each NetBackup deduplication node. The host must be a NetBackup media server. Although the storage server components run on a media server, the storage server is a separate logical entity.
Reference Architecture
For fast backup and fast restore, you should host the primary application for backup on an all-flash array-like Pure Storage® FlashArray™. Then FlashBlade acts as an NFS storage target for backups conducted by NetBackup. You can see the test architecture for Veritas NetBackup with Pure Storage arrays below.
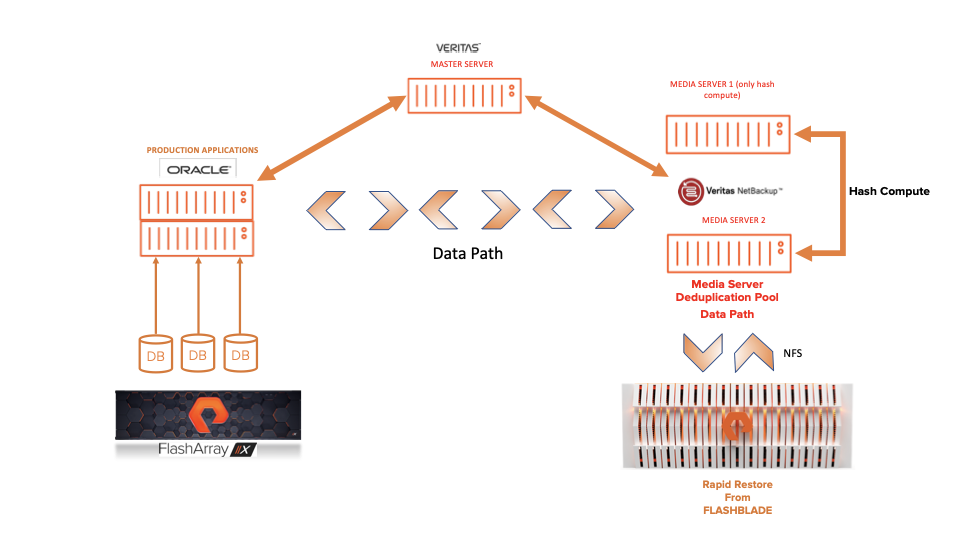
NetBackup can use FlashBlade as a target for deduplicated or non-deduplicated backups, but MSDP on FlashBlade limits the maximum size of the MSDP. While this integration supports NetBackup features, such as client-side and server deduplication, Accelerator, and Auto Image Replication (AIR), it doesn’t support instant access or universal shares.
FlashBlade as an NFS Target
Configuring FlashBlade as an NFS target for NetBackup involves creating data volume(s), an MSDP metadata volume, a NetBackup catalog volume, and exporting the volume(s) as an NFS share to the host acting as a media server. These shares are then mounted on the media server and configured as one MSDP and will serve as a target storage unit for data and catalog backups. Implementing multiple volumes allows for additional parallelism and paths to FlashBlade.
Configuring MSDP on NetBackup
Follow these steps to set up the MSDP:
- Create NFS filesystems on FlashBlade (I recommend eight filesystems for data backup and one filesystem for MSDP metadata).
- Create the appropriate mount points directories on the media server, one for each NFS data filesystem (eight) and one for the MSDP filesystem.
- Mount all the NFS on the media server while using different data VIPs on FlashBlade. For example, NFS FS1 is mounted on directory /msdp/vol1, NFS FS2 on /msdp/vol2, and so on until each volume is mounted, along with NFS for metadata on /msdp/metdata-vol.
- Create a touch a file /etc/nbapp-release if it doesn’t exist.
- Create a subdirectory – ‘data’ under each mounted volume ex: /msdp/vol1/data, /msdp/vol2/data, /msdp/vol3/data, and so on.
- Configure the MSDP using the Storage Server Configuration Wizard. Be sure to select the Use alternate path for deduplication database option.
To create and configure the Media Server Deduplication Pool via GUI and the Wizard, please follow these steps:
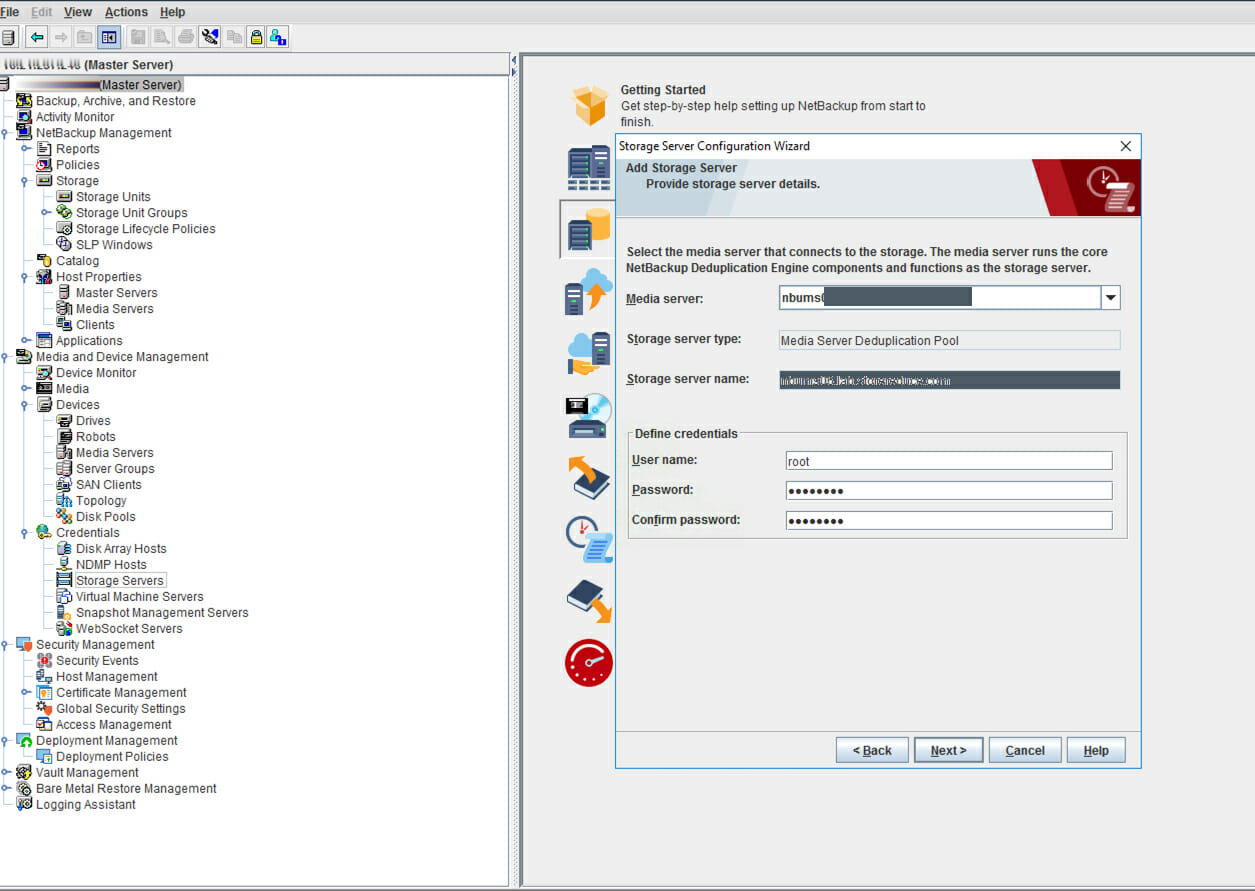
- Choose Media Server and type your user name and password. Click Next. Do not select NetBackup Master Server.
- Choose a storage path and a deduplication database path. For better performance, use a separate FlashBlade NFS mount point for the MSDP metadata and click Next.
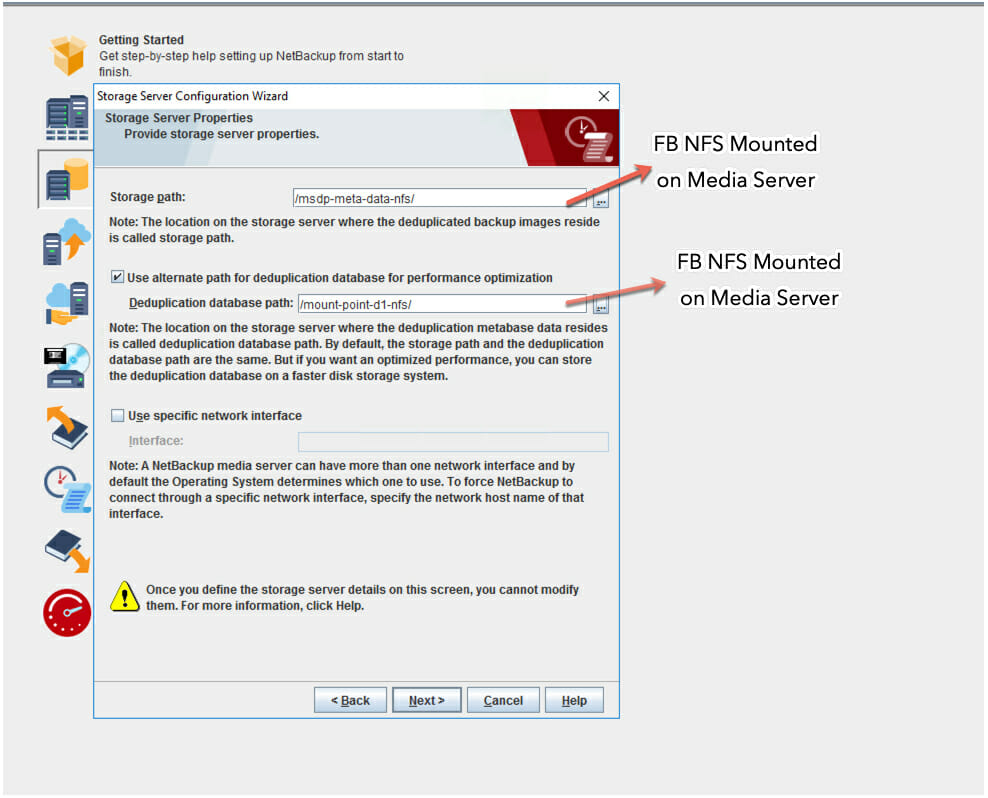
- Make sure you don’t select the NetBackup encryption option since FlashBlade has its own encryption enabled by default.
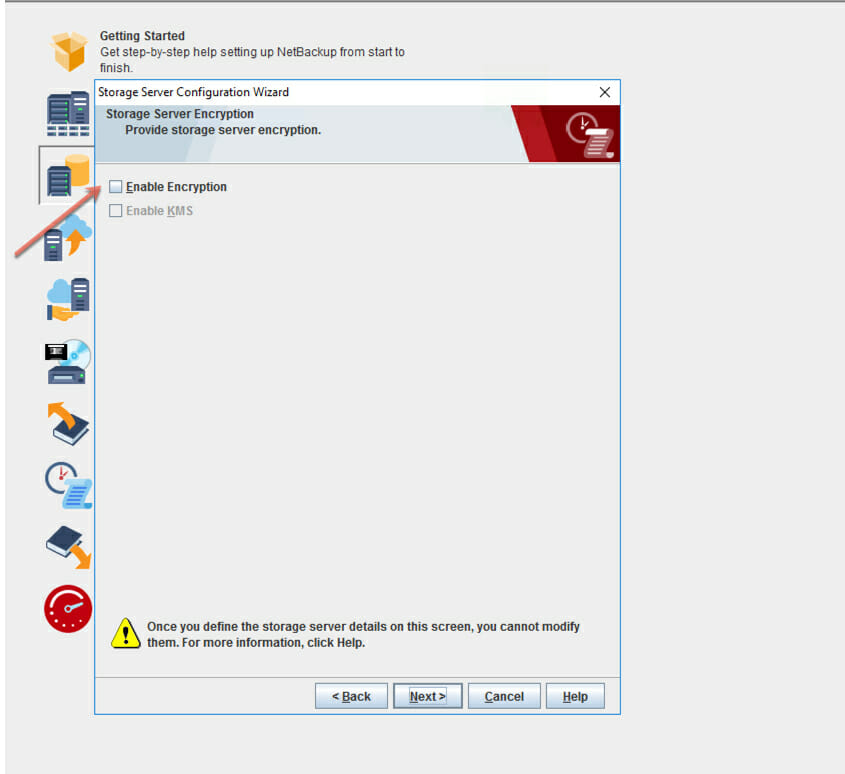
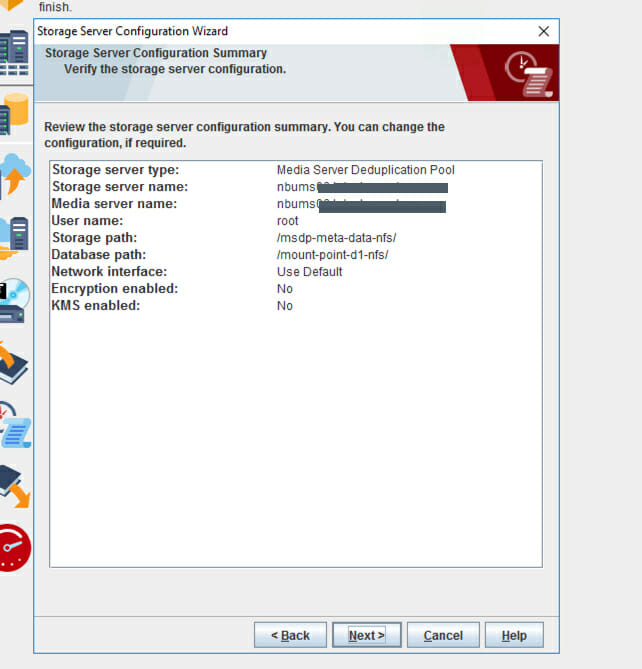
- Review the storage server configuration summary. Click Next.
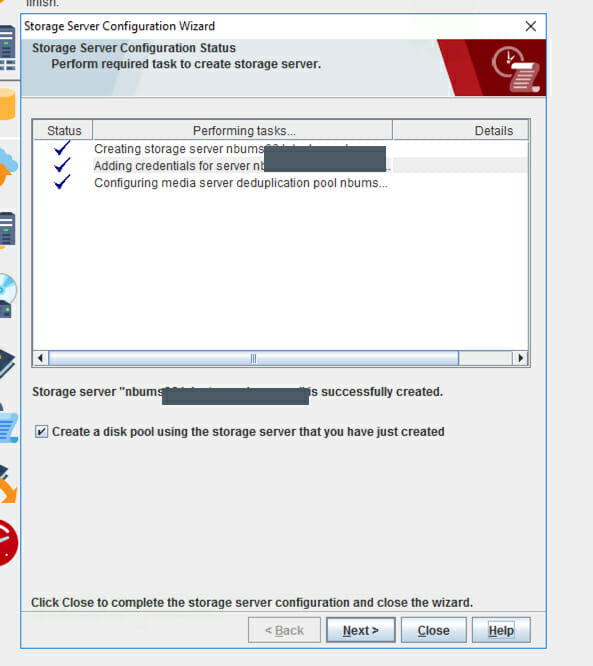
- Please wait while the wizard finishes creating the storage server. Then, click Next to start the wizard to create a disk pool.
- Add the additional data NFS filesystem mounted on the media server into the MSDP by using the following command:
|
1 |
/usr/openv/pdde/pdcr/bin/crcontrol —dsaddpartition /msdp/vol2/data |
|
1 |
/usr/openv/pdde/pdcr/bin/crcontrol —dsaddpartition /msdp/vol3/data |
Repeat this step through vol8.
The MSDP configuration is now complete. To verify that the deduplication pool contains the new volumes, review the following command:
|
1 |
/usr/openv/pdde/pdcr/bin/crcontrol —dsstat 2 |
Best Practices: Provisioning NFS FS for Deduplicated Data
When using FlashBlade as an NFS storage target for deduplicated data, performance increases by employing multiple volumes exported to multiple shares with different data virtual IP addresses and combining them into one MSDP on a single media server. Implementing multiple volumes allows for additional parallelism and paths to FlashBlade. As a best practice, you should create a volume size of at least 10TB on the FB NFS for MSDP when utilizing multiple volumes in a single MSDP. Also, the number of filesystems per MSDP should be no more than eight, which is the limitation with NetBackup MSDP.
Currently, this integration supports limited backend storage capacity (after dedupe). For more information on capacity, please contact Pure at 800-379-7873.
Takeaway
If you’re seeking an efficient storage solution that provides “rapid restore” of your environment, FlashBlade as an NFS storage target for NetBackup deduplicated data is a great option. Sending NetBackup deduplicated data to FlashBlade over NFS enables you to:
- Achieve superior rapid restore performance with FlashBlade, and support multiple, concurrent backup and restore operations that take advantage of FlashBlade as a storage platform for NetBackup.
- Gain support for key NetBackup features, such as client-side and server deduplication, Accelerator, and AIR.
- Improve storage efficiency when utilizing both NetBackup and FlashBlade compression.